HBase基础
HBase简介
HBase 定义
HBase 是一种分布式、可扩展、支持海量数据存储的 NoSQL 数据库。
HBase 数据模型
逻辑上,HBase 的数据模型同关系型数据库很类似,数据存储在一张表中,有行有列。但从HBase 的底层物理存储结构(K-V)来看,HBase 更像是一个 multi-dimensional map。
HBase 逻辑结构
HBase 物理存储结构
数据模型
Name Space
命名空间,类似于关系型数据库的 DatabBase 概念,每个命名空间下有多个表。HBase 有两个自带的命名空间,分别是 hbase 和 default,hbase 中存放的是 HBase 内置的表,default 表是用户默认使用的命名空间。
Region
类似于关系型数据库的表概念。不同的是,HBase 定义表时只需要声明列族即可,不需要声明具体的列。这意味着,往 HBase 写入数据时,字段可以动态、按需指定。因此,和关系型数据库相比,HBase 能够轻松应对字段变更的场景。
Row
HBase 表中的每行数据都由一个 RowKey 和多个 Column(列)组成,数据是按照 RowKey 的字典顺序存储的,并且查询数据时只能根据 RowKey 进行检索,所以 RowKey 的设计十分重要。
Column
HBase 中的每个列都由 Column Family(列族)和 Column Qualifier(列限定符)进行限定,例如 info:name,info:age。建表时,只需指明列族,而列限定符无需预先定义。
Time Stamp
用于标识数据的不同版本(version),每条数据写入时,如果不指定时间戳,系统会
自动为其加上该字段,其值为写入 HBase 的时间。
Cell
由{rowkey, column Family:column Qualifier, time Stamp} 唯一确定的单元。cell 中的数据是没有类型的,全部是字节码形式存贮。
HBase 基本架构

架 构 角 色 :
Region Server
Region Server 为 Region 的管理者,其实现类为 HRegionServer,主要作用如下:
对于数据的操作:get, put, delete;
对于 Region 的操作:splitRegion、compactRegion。
Master
Master 是所有 Region Server 的管理者,其实现类为 HMaster,主要作用如下:
对于表的操作:create, delete, alter
对于RegionServer 的操作:分配regions 到每个RegionServer,监控每个RegionServer的状态,负载均衡和故障转移。
Zookeeper
HBase 通过 Zookeeper 来做 Master 的高可用、RegionServer 的监控、元数据的入口以及集群配置的维护等工作。
HDFS
HDFS 为 HBase 提供最终的底层数据存储服务,同时为HBase 提供高可用的支持。
HBase 快速入门
HBase 安装部署
Zookeeper 正常部署
首先保证 Zookeeper 集群的正常部署,并启动之:
1 | [lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 zookeeper-3.4.10]$ bin/zkServer.sh start |
Hadoop 正常部署
Hadoop 集群的正常部署并启动:
1 | [lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/start-dfs.sh |
HBase 的解压
解压Hbase 到指定目录:
1 | [lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 software]$ tar -zxvf hbase-1.3.1-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/module |
HBase 的配置文件
修改HBase 对应的配置文件。
hbase-env.sh 修改内容:
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 software]$ cd /opt/module/hbase/conf
1
2
3
4
5export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_212
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false
# 在2.0.5版本中下面内容已经自动注释
#export HBASE_MASTER_OPTS="$HBASE_MASTER_OPTS -XX:PermSize=128m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m"
#export HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS="$HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS -XX:PermSize=128m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m"hbase-site.xml 修改内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29<configuration>
<!-- 这里要写你的hadoop的端口号,hadoop3.1.3使用的端口号是8020,如果不知道查看core-site.xml 文件 -->
<property>
<name>hbase.rootdir</name>
<value>hdfs://hadoop102:8020/HBase</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<!-- 0.98 后的新变动,之前版本没有.port,默认端口为 60000 -->
<property>
<name>hbase.master.port</name>
<value>16000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>hadoop102,hadoop103,hadoop104</value>
</property>
<!-- 这里需要配置你的zookeeper版本 -->
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.property.dataDir</name>
<value>/opt/module/zookeeper-3.5.7/zkData</value>
</property>
</configuration>regionservers:
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 conf]$ vim regionservers
1
2
3hadoop102
hadoop103
hadoop104软连接hadoop 配置文件到HBase
1
2[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 module]$ ln -s /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml /opt/module/hbase/conf/core-site.xml
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 module]$ ln -s /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml /opt/module/hbase/conf/hdfs-site.xml
HBase 远程发送到其他集群
1 | [lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 module]$ xsync /opt/module/hbase/ |
HBase 服务的启动
启动方式1
1
2[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ bin/hbase-daemon.sh start master
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ bin/hbase-daemon.sh start regionserver提示: 如果集群之间的节点时间不同步, 会导致 regionserver 无法启动, 抛出ClockOutOfSyncException 异常。
修复提示:
同步时间服务
请参看帮助文档:《尚硅谷大数据技术之 Hadoop 入门》
属性:hbase.master.maxclockskew 设置更大的值
启动方式 2
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ bin/start-hbase.sh
对应的停止服务:
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ bin/stop-hbase.sh
查看 HBase 页面
HBase Shell 操作
2.2.1基本操作
进入 HBase 客户端命令行
1 | [lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ bin/hbase shell |
查看帮助命令
1 | hbase(main):001:0> help |
3.查看当前数据库中有哪些表
1 | hbase(main):002:0> list |
表的操作
创建表
1
hbase(main):002:0> create 'student','info'
插入数据到表
1
2
3
4
5hbase(main):003:0> put 'student','1001','info:sex','male'
hbase(main):004:0> put 'student','1001','info:age','18'
hbase(main):005:0> put 'student','1002','info:name','Janna'
hbase(main):006:0> put 'student','1002','info:sex','female'
hbase(main):007:0> put 'student','1002','info:age','20'扫描查看表数据
1
2
3hbase(main):008:0> scan ' student'
hbase(main):009:0> scan 'student',{STARTROW => '1001', STOPROW => '1001'}
hbase(main):010:0> scan 'student',{STARTROW => '1001'}查看表结构
1
hbase(main):011:0> describe ‘student’
更新指定字段的数据
1
2hbase(main):012:0> put 'student','1001','info:name','Nick'
hbase(main):013:0> put 'student','1001','info:age','100'查看“指定行”或“指定列族:列”的数据
1
hbase(main):014:0> get 'student','1001' hbase(main):015:0> get 'student','1001','info:name'
统计表数据行数
1
hbase(main):021:0> count 'student'
删除数据
删除某 rowkey 的全部数据:
1
hbase(main):016:0> deleteall 'student','1001'
删除某 rowkey 的某一列数据:
清空表数据
1
hbase(main):018:0> truncate 'student'
提示:清空表的操作顺序为先 disable,然后再 truncate。
删除表
首先需要先让该表为 disable 状态:
1
hbase(main):019:0> disable 'student'
然后才能 drop 这个表:
1
hbase(main):020:0> drop 'student'
提示:如果直接 drop 表,会报错:ERROR: Table student is enabled. Disable it first.
变更表信息
将 info 列族中的数据存放 3 个版本:
1
2hbase(main):022:0> alter 'student',{NAME=>'info',VERSIONS=>3}
hbase(main):022:0> get'student','1001',{COLUMN=>'info:name',VERSIONS=>3}
HBase 进 阶
架构原理
StoreFile
保存实际数据的物理文件,StoreFile 以 HFile 的形式存储在 HDFS 上。每个 Store 会有一个或多个 StoreFile(HFile),数据在每个 StoreFile 中都是有序的。
MemStore
写缓存,由于 HFile 中的数据要求是有序的,所以数据是先存储在 MemStore 中,排好序后,等到达刷写时机才会刷写到HFile,每次刷写都会形成一个新的HFile。
WAL
由于数据要经 MemStore 排序后才能刷写到 HFile,但把数据保存在内存中会有很高的概率导致数据丢失,为了解决这个问题,数据会先写在一个叫做 Write-Ahead logfile 的文件中,然后再写入 MemStore 中。所以在系统出现故障的时候,数据可以通过这个日志文件重建。
写流程
写流程:
Client 先访问 zookeeper,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个Region Server。
访问对应的 Region Server,获取 hbas e:meta 表,根据读请求的 namespace:table/rowkey, 查询出目标数据位于哪个 Region Server 中的哪个 Region 中。并将该 table 的 region 信息以及 meta 表的位置信息缓存在客户端的 meta cache,方便下次访问。
与目标Region Server 进行通讯;
将数据顺序写入(追加)到 WAL;
将数据写入对应的 MemStore(如果失败WAL和MemStore都要回滚),数据会在 MemStore 进行排序;
向客户端发送ack;
MemStore Flush
MemStore Flush

MemStore 刷写时机:
当某个 memstroe 的大小达到了 hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size(默认值 128M), 其所在 region 的所有 memstore 都会刷写。
当 memstore 的大小达到了
hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size(默认值 128M)*hbase.hregion.memstore.block.multiplier(默认值 4)时,会阻止继续往该 memstore 写数据,也就是单个memstroe达到128M的时候开始刷写,到达128*4的时候停止向memstroe写数据。当region server 中 memstore 的总大小达到
java_heapsize*hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size(默认值 0.4)*hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size.lower.limit(默认值 0.95)region 会按照其所有 memstore 的大小顺序(由大到小)依次进行刷写。直到 region server中所有 memstore 的总大小减小到上述值以下。当 region server 中memstore 的总大小达到
java_heapsize*hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size(默认值 0.4)时,会阻止继续往所有的memstore 写数据,也就是memstore 的总大小达到堆内存的0.4*0.95的时候,开始刷写,达到堆内存的0.4的时候停止向所有的memstore 写数据。到达自动刷写的时间,也会触发 memstore flush。自动刷新的时间间隔由该属性进行配置 hbase.regionserver.optionalcacheflushinterval(默认 1 小时)。
当 WAL 文件的数量超过
hbase.regionserver.max.logs,region 会按照时间顺序依次进行刷写,直到 WAL 文件数量减小到hbase.regionserver.max.log以下(该属性名已经废弃, 现无需手动设置,最大值为 32)。
读流程
读流程
Client 先访问 zookeeper,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个Region Server。
访问对应的 Region Server,获取 hbase:meta 表,根据读请求的 namespace:table/rowkey, 查询出目标数据位于哪个 Region Server 中的哪个 Region 中。并将该 table 的 region 信息以及 meta 表的位置信息缓存在客户端的 meta cache,方便下次访问。
与目标Region Server 进行通讯;
分别在Block Cache(读缓存),MemStore 和 Store File(HFile)中查询目标数据,并将查到的所有数据进行合并。此处所有数据是指同一条数据的不同版本(time stamp)或者不同的类型(Put/Delete)。
将从文件中查询到的数据块(Block,HFile 数据存储单元,默认大小为 64KB)缓存到Block Cache。
将合并后的最终结果返回给客户端。
StoreFile Compaction
由于memstore 每次刷写都会生成一个新的HFile,且同一个字段的不同版本(timestamp)和不同类型(Put/Delete)有可能会分布在不同的HFile 中,因此查询时需要遍历所有的 HFile。为了减少 HFile 的个数,以及清理掉过期和删除的数据,会进行 StoreFile Compaction。
Compaction 分为两种,分别是 Minor Compaction 和 Major Compaction。Minor Compaction会将临近的若干个较小的 HFile 合并成一个较大的 HFile,但不会清理过期和删除的数据。Major Compaction 会将一个 Store 下的所有的 HFile 合并成一个大 HFile,并且会清理掉过期和删除的数据。
Region Split

默认情况下,每个 Table 起初只有一个Region,随着数据的不断写入,Region 会自动进行拆分。刚拆分时,两个子 Region 都位于当前的 Region Server,但处于负载均衡的考虑, HMaster 有可能会将某个 Region 转移给其他的 Region Server。
Region Split 时机:
- 当1 个region 中的某个Store 下所有StoreFile 的总大小超过hbase.hregion.max.filesize, 该 Region 就会进行拆分(0.94 版本之前)。
- 当 1 个 region 中的某个 Store 下所有 StoreFile 的总大小超过 Min(R^2 * “hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size”,hbase.hregion.max.filesize”),该 Region 就会进行拆分,其中 R 为当前 Region Server 中属于该 Table 的个数(0.94 版本之后)。
- 生产环境中我们不用自动分区,我们在创建表的时候就预分区(类似于hive的分区表),防止数据倾斜
注意:在生产环境官方不建议使用多个列族,因为有可能一个列族中的数据特别多,而其他列族中的数据几乎没有,那么在全局flush的时候就会生成大量的小文件。但是如果我们在生产环境中控制好让多个列族的数据均匀放置,那么使用多个列族是没有问题的。
HBase API
环境准备
新建项目后在pom.xml 中添加依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
HBaseAPI
1 | public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { |
获取 Configuration 对象
1 | private static Connection connection = null; |
判断表是否存在
1 | public static boolean isTableExist(String tableName) throws MasterNotRunningException, ZooKeeperConnectionException, IOException { |
创建表
1 | public static void createTable(String tableName, String... columnFamily) throws MasterNotRunningException, ZooKeeperConnectionException, IOException { |
删除表
1 | public static void dropTable(String tableName) throws MasterNotRunningException, ZooKeeperConnectionException, IOException { |
创建命名空间
1 | public static void creatNameSpace(String nameSpace) { |
向表中插入数据
1 | public static void addRowData(String tableName, |
删除指定数据
也可以删除指定列族
1 | public static void deleteMultiRow(String tableName, String rowKey,String columnFamily,String column) |
删除多行数据
1 | public static void deleteMultiRow(String tableName, String... rows) |
总结:
可以删除指定列族,这里会直接删除多个版本
可以删除指定列族下的rowkey,删除多个版本
删除指定列中的column,推荐使用addColumns,删除所有版本(防止出现数据复活),如果使用addColumn则默认删除最新版本的数据(可以指定时间戳,删除指定版本)
获取所有数据
1 | public static void getAllRows(String tableName) throws IOException { |
获取某一行数据
1 | public static void getRow(String tableName, String rowKey) throws |
获取某一行指定“列族:列”的数据
1 | public static void getRowQualifier(String tableName, |
MapReduce
通过 HBase 的相关 JavaAPI,我们可以实现伴随 HBase 操作的 MapReduce 过程,比如使用MapReduce 将数据从本地文件系统导入到 HBase 的表中,比如我们从 HBase 中读取一些原始数据后使用 MapReduce 做数据分析。
官方 HBase-MapReduce
查看 HBase 的 MapReduce 任务的执行
1
$ bin/hbase mapredcp
环境变量的导入
执行环境变量的导入(临时生效,在命令行执行下述操作)
1
2
3$ export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hbase
$ export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3
$ export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase mapredcp`永久生效:在/etc/profile 配置
1
2export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hbase
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3并在 hadoop-env.sh 中配置:(注意:在 for 循环之后配)
1
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:/opt/module/hbase/lib/*
运行官方的 MapReduce 任务
– 案例一:统计 案例一:统计 Student表中有多少行数据 表中有多少行数据 表中有多少行数据 表
1
$ /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/bin/yarn jar lib/hbase-server-1.3.1.jar rowcounter student
案例二:使用 MapReduce 将本地数据导入到 HBase
在本地创建一个 tsv 格式的文件:fruit.tsv
1
2
31001 Apple Red
1002 Pear Yellow
1003 Pineapple Yellow创建Hbase 表
1
Hbase(main):001:0> create 'fruit','info'
在HDFS 中创建 input_fruit 文件夹并上传 fruit.tsv 文件
1
2$ /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /input_fruit/
$ /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/bin/hdfs dfs -put fruit.tsv /input_fruit/执行 MapReduce 到HBase 的 fruit 表中
1
2
3$ /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/bin/yarn jar lib/hbase-server-1.3.1.jar importtsv \
-Dimporttsv.columns=HBASE_ROW_KEY,info:name,info:color fruit \
hdfs://hadoop102:9000/input_fruit使用 scan 命令查看导入后的结果
1
Hbase(main):001:0> scan ‘fruit’
自定义HBase-MapReduce1
目标:将 fruit 表中的一部分数据,通过 MR 迁入到 fruit_mr 表中。分步实现:
构建 FruitMapper类,用于读取fruit 表中的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35package top.lvxiaoyi.mr1;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.Cell;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.CellUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FruitMapper extends TableMapper<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put>{
protected void map(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Result value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//构建Put对象
Put put = new Put(key.get());
//遍历数据
Cell[] cells = value.rawCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
if ("name".equals(Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)))){
put.add(cell);
}
}
//写出去
context.write(key, put);
}
}构建 WriteFruitMRReducer 类,用于将读取到的 fruit 表中的数据写入到 fruit_mr 表 中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22package top.lvxiaoyi.mr1;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FruitReducer extends TableReducer<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put, NullWritable>{
protected void reduce(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Iterable<Put> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//遍历写出
for (Put value : values) {
context.write(NullWritable.get(), value);
}
}
}构建 FruitDriver用于组装运行 Job任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61package top.lvxiaoyi.mr1;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapReduceUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
public class FruitDriver extends Configuration implements Tool {
private Configuration configuration = null;
public int run(String[] strings) throws Exception {
//1.设置job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
//2.设置Driver类
job.setJarByClass(FruitDriver.class);
//3. 设置Mapper,和输出的kv类型
// 这里可以使用hadoop阶段学习的固定套路,也可以使用下面的方式,推荐使用util类
// job.setMapperClass(FruitMapper.class);
// job.setMapOutputKeyClass(ImmutableBytesWritable.class);
// job.setMapOutputValueClass(Put.class);
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableMapperJob("fruit", new Scan(), FruitMapper.class, ImmutableBytesWritable.class, Put.class, job);
//指定Reducer
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob("fruit_mr", FruitReducer.class, job);
//提交
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return b ? 0 : 1;
}
public void setConf(Configuration conf) {
this.configuration = conf;
}
public Configuration getConf() {
return configuration;
}
//4.主函数中调用运行该 Job 任务
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
int i = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new FruitDriver(), args);
}
}打包运行任务
1
$ /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/bin/yarn jar ~/softwares/jars/Hbase-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar top.lvxiaoyi.mr1.FruitDriver
提示:运行任务前,如果待数据导入的表不存在,则需要提前创建。
提示:maven 打包命令:-P local clean package 或-P dev clean package install(将第三方 jar 包一同打包,需要插件:maven-shade-plugin)- 创建数据库
1
create 'fruit_mr','info'
自定义 Hbase-MapReduce2
目标:实现将 HDFS 中的数据写入到 Hbase 表中。
分步实现:
构建 HDFSMapper于读取 HDFS 中的文件数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36package top.lvxiaoyi.mr2;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HDFSMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, Put> {
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取一行数据
String line = value.toString();
//切割
String[] split = line.split("\t");
//封装Put对象
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(split[0]));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes(split[1]));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("color"), Bytes.toBytes(split[2]));
//写出
context.write(NullWritable.get(), put);
}
}构建 HDFSReducer 类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21package top.lvxiaoyi.mr2;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HDFSReducer extends TableReducer<NullWritable, Put,NullWritable>{
protected void reduce(NullWritable key, Iterable<Put> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//遍历写出
for (Put value : values) {
context.write(NullWritable.get(), value);
}
}
}创建 HDFSDriver组装 Job
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61package top.lvxiaoyi.mr2;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapReduceUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
public class HDFSDriver extends Configuration implements Tool {
private Configuration configuration = null;
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取Job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
//设置主类
job.setJarByClass(HDFSDriver.class);
//设置Mapper
job.setMapperClass(HDFSMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Put.class);
//设置Reducer
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob("fruit2", HDFSReducer.class, job);
//设置输入路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, args[0]);
//提交
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return result ? 0 : 1;
}
public void setConf(Configuration conf) {
configuration = conf;
}
public Configuration getConf() {
return configuration;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
int i = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new HDFSDriver(), args);
System.exit(i);
}
}打包运行
1
2
3$ /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/bin/yarn jar hbase-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar top.lvxiaoyi.mr2.HDFSDriver /fruit.tsv
$ /opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/bin/yarn jar Hbase01-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar top.lvxiaoyi.mr2.HDFSDriver file:///opt/module/hbase/fruit.tsv提示:运行任务前,如果待数据导入的表不存在,则需要提前创建之。
提示:maven 打包命令:-P local clean package 或 -P dev clean package install(将第三方 jar 包一同打包,需要插件:maven-shade-plugin)
与 Hive 的集成
HBase 与 Hive 的对比
Hive
- 数据仓库Hive 的本质其实就相当于将 HDFS 中已经存储的文件在 Mysql 中做了一个双射关系,以方便使用 HQL 去管理查询。
- 用于数据分析、清洗Hive 适用于离线的数据分析和清洗,延迟较高。
- 基于 HDFS、MapReduceHive 存储的数据依旧在 DataNode 上,编写的 HQL 语句终将是转换为 MapReduce 代码执行。
HBase
- 数据库是一种面向列族存储的非关系型数据库。
- 用于存储结构化和非结构化的数据适用于单表非关系型数据的存储,不适合做关联查询,类似 JOIN 等操作。
- 基于 HDFS数据持久化存储的体现形式是 HFile,存放于 DataNode 中,被 RegionServer 以 region 的形式进行管理。
- 延迟较低,接入在线业务使用面对大量的企业数据,HBase 可以直线单表大量数据的存储,同时提供了高效的数据访问速度。
HBase 与 Hive 集成使用
尖叫提示:HBase 与 Hive 的集成在最新的两个版本中无法兼容。所以,我们只能含着泪勇敢的重新编译:hive-hbase-handler-1.2.2.jar!!好气!!,把这个jar包直接覆盖
环境准备因为我们后续可能会在操作 Hive 的同时对 HBase 也会产生影响,所以 Hive 需要持有操作HBase 的 Jar,那么接下来拷贝 Hive 所依赖的 Jar 包(或者使用软连接的形式)
1 | export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hbase |
同时在 hive-site.xml 中修改 zookeeper 的属性,如下:
1 | <property> |
注意:
- 最终的数据是保存在HBase中的
- 要注意的是这两个表的数据类型要关联,要不然是null,hive是有数据类型的,而hbase是没有数据类型的
案例一
目标:建立 Hive 表,关联 HBase 表,插入数据到 Hive 表的同时能够影响 HBase 表,
分步实现:
在 Hive 中创建表同时关联 HBase
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13CREATE TABLE hive_hbase_emp_table(
empno int,
ename string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("hbase.columns.mapping" =
":key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:comm,info:deptno")
TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name" = "hbase_emp_table");提示:完成之后,可以分别进入 Hive 和 HBase 查看,都生成了对应的表
STORED BY ‘org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler’:建立hive和hbase的关系
“:key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:comm,info:deptno”):hive的关键字和hbase的关系一一对应映射,:key是关键字
TBLPROPERTIES (“hbase.table.name” = “hbase_emp_table”):设置HBase表的名字
在 Hive 中创建临时中间表,用于 load 文件中的数据
提示:不能将数据直接 load 进 Hive 所关联 HBase 的那张表中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10CREATE TABLE emp(
empno int,
ename string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';向 Hive 中间表中 load 数据
1
hive> load data local inpath '/home/admin/softwares/data/emp.txt' into table emp;
通过 insert 命令将中间表中的数据导入到 Hive 关联 Hbase 的那张表中
1
hive> insert into table hive_hbase_emp_table select * from emp;
查看 Hive 以及关联的 HBase 表中是否已经成功的同步插入了数据
1
2
3
4
5Hive:
hive> select * from hive_hbase_emp_table;
HBase:
Hbase> scan ‘hbase_emp_table’
案例二
目标:在 HBase 中已经存储了某一张表 hbase_emp_table,然后在 Hive 中创建一个外部表来关联 HBase 中的 hbase_emp_table 这张表,使之可以借助 Hive 来分析 HBase 这张表中的数据。
注:该案例 2 紧跟案例 1 的脚步,所以完成此案例前,请先完成案例 1。
在 Hive 中创建外部表
主要是关键字:EXTERNAL
建立一个外部表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE relevance_hbase_emp(
empno int,
ename string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int)
STORED BY
'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("hbase.columns.mapping" =
":key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:comm,info:deptno")
TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name" = "hbase_emp_table");关联后就可以使用 Hive 函数进行一些分析操作了
1
hive (default)> select * from relevance_hbase_emp;
HBase 优化
高可用
在 HBase 中 HMaster 负责监控 HRegionServer 的生命周期,均衡 RegionServer 的负载,如果 HMaster 挂掉了,那么整个 HBase 集群将陷入不健康的状态,并且此时的工作状态并不会维持太久。所以 HBase 支持对 HMaster 的高可用配置。
关闭 HBase 集群(如果没有开启则跳过此步)
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ bin/stop-hbase.sh
在 conf 目录下创建 backup-masters 文件
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ touch conf/backup-masters
在 backup-masters 文件中配置高可用 HMaster 节点
1
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ echo hadoop103 > conf/backup-masters
将整个 conf 目录 scp 到其他节点
1
2
3
4[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ scp -r conf/
hadoop103:/opt/module/hbase/
[lvxiaoyi@hadoop102 hbase]$ scp -r conf/
hadoop104:/opt/module/hbase/打开页面测试查看
http://hadooo102:16010
预分区
每一个 region 维护着 StartRow 与 EndRow,如果加入的数据符合某个 Region 维护的RowKey 范围,则该数据交给这个 Region 维护。那么依照这个原则,我们可以将数据所要投放的分区提前大致的规划好,以提高 HBase 性能。
手动设定预分区
1
Hbase> create 'staff1','info','partition1',SPLITS => ['1000','2000','3000','4000']
生成 16 进制序列预分区
1
2create 'staff2','info','partition2',{NUMREGIONS => 15, SPLITALGO =>
'HexStringSplit'}按照文件中设置的规则预分区
创建 splits.txt 文件内容如下:
1
2
3
4aaaa
bbbb
cccc
dddd然后执行:
1
create 'staff3','partition3',SPLITS_FILE => 'splits.txt'
使用 JavaAPI 创建预分区
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8//自定义算法,产生一系列 hash 散列值存储在二维数组中
byte[][] splitKeys = 某个散列值函数
//创建 HbaseAdmin 实例
HBaseAdmin hAdmin = new HBaseAdmin(HbaseConfiguration.create());
//创建 HTableDescriptor 实例
HTableDescriptor tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(tableName);
//通过 HTableDescriptor 实例和散列值二维数组创建带有预分区的 Hbase 表
hAdmin.createTable(tableDesc, splitKeys);
RowKey 设计
一条数据的唯一标识就是 RowKey,那么这条数据存储于哪个分区,取决于 RowKey 处于哪个一个预分区的区间内,设计 RowKey 的主要目的 ,就是让数据均匀的分布于所有的region 中,在一定程度上防止数据倾斜。
例如:手机号的通话记录时长,如果只是使用手机号的前面数字分区,还是有可能产生数据倾斜,因为你的所有历史都是在一个里面,这样我们可以使用手机号+时间戳的形式分区
接下来我们就谈一谈 RowKey 常用的设计方案。
生成随机数、hash、散列值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9比如:
原 本 rowKey 为 1001 的 , SHA1 后 变 成 :
dd01903921ea24941c26a48f2cec24e0bb0e8cc7
原 本 rowKey 为 3001 的 , SHA1 后 变 成 :
49042c54de64a1e9bf0b33e00245660ef92dc7bd
原 本 rowKey 为 5001 的 , SHA1 后 变 成 :
7b61dec07e02c188790670af43e717f0f46e8913
在做此操作之前,一般我们会选择从数据集中抽取样本,来决定什么样的 rowKey 来 Hash
后作为每个分区的临界值。字符串反转
20170524000001 转成 10000042507102
20170524000002 转成 20000042507102
这样也可以在一定程度上散列逐步 put 进来的数据。
字符串拼接
20170524000001_a12e
20170524000001_93i7
内存优化
HBase 操作过程中需要大量的内存开销,毕竟 Table 是可以缓存在内存中的,一般会分配整个可用内存的 70%给 HBase 的 Java 堆。但是不建议分配非常大的堆内存,因为 GC 过程持续太久会导致 RegionServer 处于长期不可用状态,一般 16~48G 内存就可以了,如果因为框架占用内存过高导致系统内存不足,框架一样会被系统服务拖死。
基础优化
允许在 HDFS 的文件中追加内容
hdfs-site.xml、hbase-site.xml
属性:dfs.support.append
解释:开启 HDFS 追加同步,可以优秀的配合 HBase 的数据同步和持久化。默认值为 true。
优化 DataNode 允许的最大文件打开数
hdfs-site.xml
属性:dfs.datanode.max.transfer.threads
解释:HBase 一般都会同一时间操作大量的文件,根据集群的数量和规模以及数据动作,
设置为 4096 或者更高。默认值:4096
优化延迟高的数据操作的等待时间
hdfs-site.xml
属性:dfs.image.transfer.timeout
解释:如果对于某一次数据操作来讲,延迟非常高,socket 需要等待更长的时间,建议把该值设置为更大的值(默认 60000 毫秒),以确保 socket 不会被 timeout 掉。
优化数据的写入效率
mapred-site.xml
属性:mapreduce.map.output.compressmapreduce.map.output.compress.codec
解释:开启这两个数据可以大大提高文件的写入效率,减少写入时间。第一个属性值修改为true,第二个属性值修改为:org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec 或者其他压缩方式。
设置 RPC 监听数量
hbase-site.xml
属性:Hbase.regionserver.handler.count
解释:默认值为 30,用于指定 RPC 监听的数量,可以根据客户端的请求数进行调整,读写请求较多时,增加此值。
优化 HStore 文件大小
hbase-site.xml
属性:hbase.hregion.max.filesize
解释:默认值 10737418240(10GB),如果需要运行 HBase 的 MR 任务,可以减小此值,因为一个 region 对应一个 map 任务,如果单个 region 过大,会导致 map 任务执行时间过长。该值的意思就是,如果 HFile 的大小达到这个数值,则这个 region 会被切分为两个 Hfile。
优化 HBase 客户端缓存
hbase-site.xml
属性:hbase.client.write.buffer
解释:用于指定 Hbase 客户端缓存,增大该值可以减少 RPC 调用次数,但是会消耗更多内存,反之则反之。一般我们需要设定一定的缓存大小,以达到减少 RPC 次数的目的。
指定 scan.next 扫描 HBase 所获取的行数
hbase-site.xml
属性:hbase.client.scanner.caching
解释:用于指定 scan.next 方法获取的默认行数,值越大,消耗内存越大。
flush、compact、split 机制
当 MemStore 达到阈值,将 Memstore 中的数据 Flush 进 Storefile;compact 机制则是把 flush
出来的小文件合并成大的 Storefile 文件。split 则是当 Region 达到阈值,会把过大的 Region一分为二。
涉及属性:
即:128M 就是 Memstore 的默认阈值
hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size:134217728
即:这个参数的作用是当单个 HRegion 内所有的 Memstore 大小总和超过指定值时,flush该 HRegion 的所有 memstore。RegionServer 的 flush 是通过将请求添加一个队列,模拟生产消费模型来异步处理的。那这里就有一个问题,当队列来不及消费,产生大量积压请求时,可能会导致内存陡增,最坏的情况是触发 OOM。
hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit:0.4
hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit:0.38
即:当 MemStore 使用内存总量达到hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit 指定值时,将会有多个 MemStores flush 到文件中,MemStore flush 顺序是按照大小降序执行的,直到刷新到 MemStore 使用内存略小于 lowerLimit
1 | <!-- 一个store里面允许存的hfile的个数,超过这个个数会被写到新的一个hfile里面 也即是每个region的每个列族对应的memstore在fulsh为hfile的时候,默认情况下当超过3个hfile的时候就会 |
HBase 实战之谷粒微博
1 需求分析
模拟微博运行过程,可以实现发布微博、关注/取关用户、查看用户微博内容等功能。
2 数据表设计
共设计3张表,分别是微博内容表、用户关系表、微博收件箱表。
2.1 微博内容表
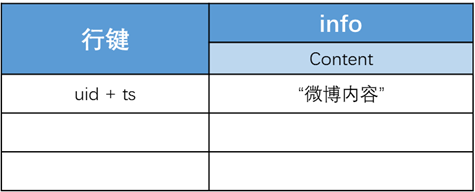
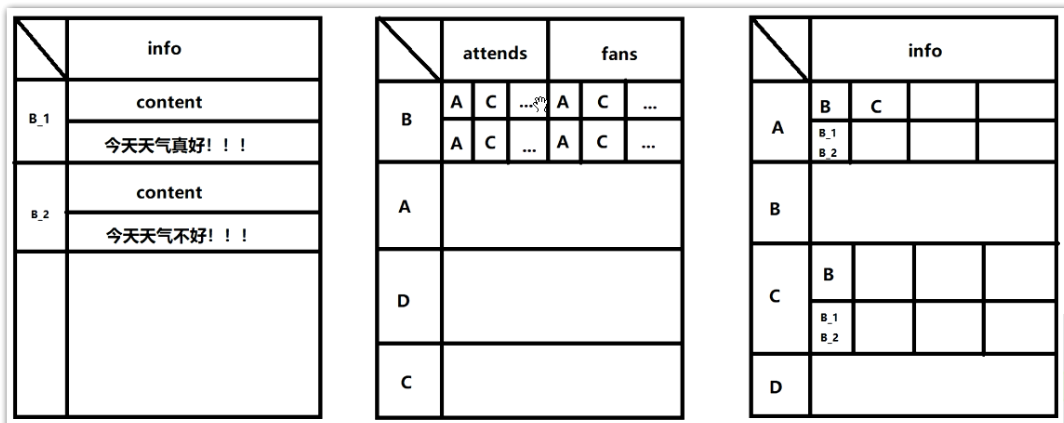
设计一个列族info,包含一个列Content,用于存放发布的微博内容。行键设计为用户id+时间戳,每行数据表示某个用户在某一时刻发布的微博内容。所有用户发布的所有微博内容均存储在一张表中。
2.2 用户关系表
设计两个列族attends、fans,表示当前用户的关注者和粉丝。每个列族可以有很多列,每个列表示一个具体的用户,列的值与列名保持相同,仅起到标识用户的作用。行键设计为用户id。如果某个用户没有关注任何其他用户,则该行数据的attends列族为空;同样地,如果没有粉丝,则fans列族为空。
2.3 微博收件箱表(初始化页面表)
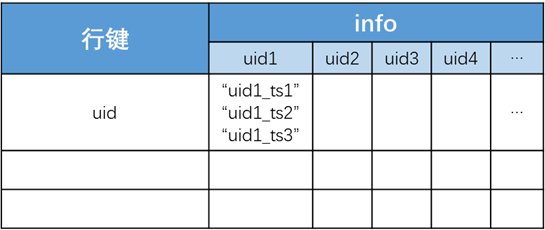
设计为一个列族info,可以包括多个列,分别表示当前用户关注的其他用户。行键设计为用户id,每行数据表示当前用户关注的其他用户所发布的微博内容,每列的值设置3个版本,内容为关注者所发布的微博内容的行键(uid+ts)。即列的值是第一张表(微博内容表)的外键。
数据表示例如下:
3 项目架构
创建Maven工程,在pom.xml文件中添加项目所需要的依赖。
1 | <dependencies> |
在src/main/resources文件夹下添加配置文件hbase-site.xml,其中包含项目要连接的集群信息,这样就不用在代码里再设置了。
1 |
|
在src/main/java下创建4个Java包:constants、utils、dao、test,分别表示常量、工具类、数据操作、测试。
4 定义常量
在constants包下创建Constants类,存放项目需要用到的常量。包括HBase配置信息、命名空间、微博内容表及其列族信息、用户关系表及其列族信息、收件箱表及其列族信息。
1 | public class Constants { |
5 BaseUtil封装
在utils包下创建HBaseUtil类,提供项目通用的功能,包括创建命名空间、判断表是否存在、创建表。
1 | public class HBaseUtil { |
6 HBaseDao封装
在dao包下创建HBaseDao类,实现与业务相关的数据操作功能。
6.1 发布微博
1 | // 1 发布微博 |
难点是要同时操作3张表,要处理3张表之间的联系。某个uid用户发布了一条微博,系统做了这些事情:在微博内容表中,添加一条数据;在用户关系表中,查找uid的fans用户;在微博收件箱表中,为所有fans用户更新当前uid用户的微博发布信息。
微博内容表中,行键设计为uid+时间戳。
1 | Table contTable = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(Constants.CONTENT_TABLE)); |
在用户关系表中,查找当前uid的fans信息。遍历每一个粉丝,在微博收件箱表中为每个粉丝更新uid用户的微博发布信息。构建Get对象,行键为uid,列族为fans,传入用户关系表中,返回一个result对象,其中包含uid的所有粉丝信息。
1 | Table relaTable = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(Constants.RELATION_TABLE)); |
解析result对象,获取每一个cell对象,每个cell对象包含列族fans中的各列的列名及列的值。将获取到的粉丝信息作为新的行键,构建微博收件箱表的Put对象,列族为info,列名为当前用户的uid,值是当前新添加微博的行键(uid+时间戳)。每一个Put对象存放在创建的ArrayList列表中。循环遍历每一个粉丝,进行如上操作。
1 | ArrayList<Put> inboxPuts = new ArrayList<>(); |
如果当前uid用户没有粉丝(ArrayList列表为空),则不对微博收件箱表做任何操作。否则,获取微博收件箱表对象,并将ArrayList列表中的Put对象传入到微博收件箱表中。
1 | // 判断当前uid是否有粉丝 |
最后,关闭资源。
1 | // 关闭资源 |
6.2 关注用户
1 | // 2 关注用户 |
关注用户同样需要操作3张表。在用户关系表中,当前uid用户在attends列族中添加若干个用户,同时这些用户在fans列族中添加当前uid用户。此外,在微博收件箱表中,以当前uid用户为行键,在列族info中添加若干个列,每列表示一个关注人,每列的值存放此关注人发布的微博的行键(版本存放2条)。
循环遍历传入的attends参数,在每一次遍历中要同时做两件事情。一是为uid添加关注人,二是为关注人添加粉丝(uid)。这个地方要注意,对于同一行数据,Put对象可以分步骤添加多个列。而对于不同行数据,需要分别创建Put对象并添加到ArrayList
1 | // 添加uid用户的关注人,且同步更新关注人的粉丝信息 |
在微博收件箱表中,对于当前uid用户,为其添加新关注的人,并更新这些人发布的微博信息。这两个信息分别由列名和列值承载,所以可以通过一个Put对象同时添加。新关注人发布的微博信息通过Scan对象获取,指定起始和终止的行键,根据字典序的排序规则以及微博内容表中“uid+时间戳”的行键设计规则,设计起始行键为“attend_”,终止行键为“attend|”,其中attend是要关注的人。这样设计可以获取到某个用户所发布的全部微博的行键(字典序,有比没有大,而且字符|大于字符_)。微博内容表的getScanner()方法返回ResultScanner对象,其中包含若干个Result对象。每一个Result对象表示一行数据,包含所需要的行键信息。手动定义一个时间戳,以解决多条数据同一时间戳的问题。最后,如果当前uid用户新关注的人都没有发布过微博,则不用对微博收件箱表做任何操作;当至少有一条微博时,才进行后续操作。
1 | // 更新微博收件箱表信息 |
6.3 取关用户
1 | // 3 取关用户 |
与关注用户逻辑类似,但更简单些,因为只涉及到用户关系表和微博收件箱表两张表。其中,调用了Delete对象的addColumns()方法而不是addColumn()方法,addColumns()方法可以同时删掉多个版本。
6.4 获取某个人的初始化页面数据
1 | // 4 获取某个人的初始化页面数据 |
根据当前uid用户遍历微博收件箱表,找到其关注的所有人,打印出这些人发布的若干条微博数据(由版本数控制)。
创建Get对象,传入uid作为行键,并设置最大版本。传入收件箱表对象,返回一个Result对象,其中包含uid所关注的所有用户的若干条微博的行键。
1 | Table contTable = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(Constants.CONTENT_TABLE)); |
获取result对象的所有Cell对象,每一个Cell对象包含一条微博数据的一个行键。遍历所有Cell对象,获取微博数据的行键,之后再微博内容表中根据行键找到相应微博数据,此时返回一个Result对象。这个Result对象只包含一个Cell对象(Cell是HBase中的概念,是由列族、列名、时间戳唯一确定的单元),获取这个Cell对象,进一步地获取行键、列族、列名、值的信息。这里的难点在于对Result和Cell的理解。
1 | for (Cell cell : result.rawCells()) { |
6.5 获取某个人的所有微博详情
1 | // 5 获取某个人的所有微博详情 |
可以使用Scan起始终止行键的方法,也可以使用过滤器的方法。这里创建一个行键过滤器RowFilter,第一个参数传入比较符,第二个参数传入要比较的对象。之后通过setFilter()方法为Scan对象添加过滤器。
1 | Scan scan = new Scan(); |
7 测试代码
在test包下新建TestWeiBo类,存放程序主函数。
1 | public class TestWeiBo { |