题目 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 输入数字 n,按顺序打印出从 1 到最大的 n 位十进制数。比如输入 3 ,则打印出 1 、2 、3 一直到最大的 3 位数 999 。 示例 1 : 输入: n = 1 输出: [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ] 说明: 用返回一个整数列表来代替打印 n 为正整数
原题目:
思路 普通的暴力解法就能够得到答案,但是这个题目原本要就是大数情况下的打印,这个n可以使无限大的。
所以这个时候不能用int去保存打印的数字,而是需要用string保存。
但是使用string也需要注意一点:
使用int类型时,每轮可以通过+1生成下一个数字,而此方法无法直接应用到string类型。并且,String类型的数字的进位操作效率较低,例如:“9999”进位到“10000”,需要从个位到千位循环判断,进位4次,效率较低。
所以最后的结果是通过String+全排列完成,避开进位操作,通过递归生成数字的String列表。
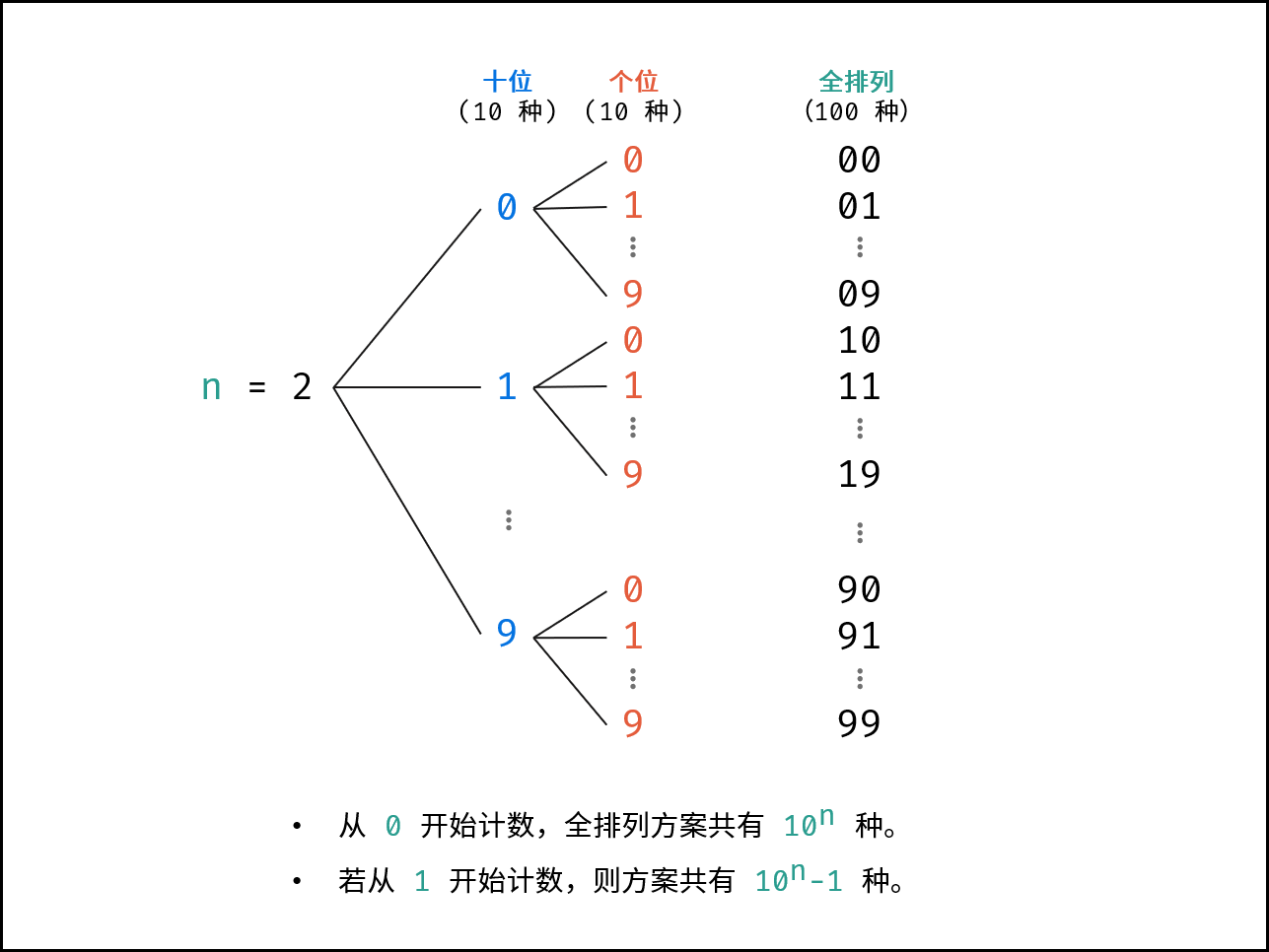
递归生成全排列:
实现 暴力解法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public int [] printNumbers(int n) { int count = getCount(n); int [] res = new int [count]; for (int i = 0 ; i < count ; i++) { res[i] = i + 1 ; } return res; } public int getCount (int n) int x = 10 ; long b = n; double res = 1.0 ; while (b > 0 ) { if ((b & 1 ) == 1 ) { res *= x; } x *= x; b >>= 1 ; } return ((int ) res - 1 ); }
使用String的暴力解法 ==注意一:如果将本题改为考虑int的范围,那么返回值应该是范围String类型的字符串==
==注意二:即便使用了string类型,在一般的电脑环境下还是会报错OOM,这种情况是考虑内存比较大的情况下,要不及时多少组的计算结果不断放入外存中==
这种直接调用string类型的“add方法”,效率低。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private static class Solution2 public String printNumbers (int n) BigInteger num = new BigInteger("1" ); StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); while (num.toString().length() <= n) { res.append(num).append("," ); num = num.add(new BigInteger("1" )); } res.replace(res.length()-1 ,res.length(),"" ); return res.toString(); } }
使用String类型的全排列 粗略 这种情况下生成的字符串,“001”,前面的0会显示,我们需要把前面的无意义的0全部去掉
注意:
这里的全排列和我们正常的那种dfs有稍微的区别,我们正常的全排列,需要判断这个数组中的数是否拿过,而这里的全排列是一个笛卡尔积,这个数还是可以取第二次的,所以我们不需要声明一个变量来判断该节点是否访问过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private static class Solution3 private int n = 0 ; public String printNumbers (int n) this .n = n; char [] path = new char [n]; char [] loop = {'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' , '6' , '7' , '8' , '9' }; int depth = 0 ; StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); dfs(depth, path, loop, res); res.replace(res.length() - 1 , res.length(), "" ); return res.toString(); } private void dfs (int depth, char [] path, char [] loop, StringBuilder res) if (depth == n) { res.append(String.valueOf(path)).append("," ); return ; } for (char c : loop) { path[depth] = c; dfs(depth + 1 , path, loop, res); } } }
1 2 000 ,001 ,002 ,003 ,004 ,005 ,006 ,007 ,008,009,.........990 ,991 ,992 ,993 ,994 ,995 ,996 ,997 ,998 ,999
优化 我们这里主要是为了把前面的0去掉。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 private static class Solution4 private int n = 0 ; public String printNumbers (int n) this .n = n; char [] path = new char [n]; char [] loop = {'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' , '6' , '7' , '8' , '9' }; int depth = 0 ; StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); dfs(depth, path, loop, res); res.replace(res.length() - 1 , res.length(), "" ); return res.toString(); } private void dfs (int depth, char [] path, char [] loop, StringBuilder res) if (depth == n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < path.length; i++) { if (path[i] != '0' ){ res.append(String.valueOf(path).substring(i)).append("," ); break ; } } return ; } for (char c : loop) { path[depth] = c; dfs(depth + 1 , path, loop, res); } } }